Philosophy in Ancient Greece was a rich and complex field, with numerous philosophers and schools of thought that sought to understand the nature of reality, ethics, politics, and the human condition. These philosophers have had a profound impact on Western civilization and continue to be studied and debated to this day. In this article, we will explore the key philosophical concepts and figures of Ancient Greece, delving into the ideas that shaped this fascinating period of intellectual inquiry.

Pre-Socratic Philosophy in Ancient Greece
The first philosophers in ancient Greece were known as the Pre-Socratics. They lived between the 7th and 5th centuries BCE and were primarily concerned with explaining the natural world. The Pre-Socratics sought to understand the underlying principles that govern the universe and the nature of existence.
These philosophers were known for their groundbreaking ideas, which challenged the traditional religious and mythological beliefs of the time. Some of the most famous pre-Socratic philosophers include Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes.
Thales was a philosopher and mathematician who is credited with being the first Greek philosopher to seek natural explanations for the phenomena of the world. His ideas laid the foundation for the development of Western science and philosophy.
Anaximander, also of Miletus, was a student of Thales. He believed that the universe was infinite and unbounded, and that it was governed by a single principle, which he called the “Apeiron”. Anaximander believed that the universe was eternal and that it was constantly changing, with new forms of life emerging and old forms dying out.
Anaximenes, another Miletian philosopher, was a student of Anaximander. He believed that air was the underlying principle of the universe, and that all things could be reduced to air in its different forms. Anaximenes believed that the universe was infinite and that air was the source of life and movement.
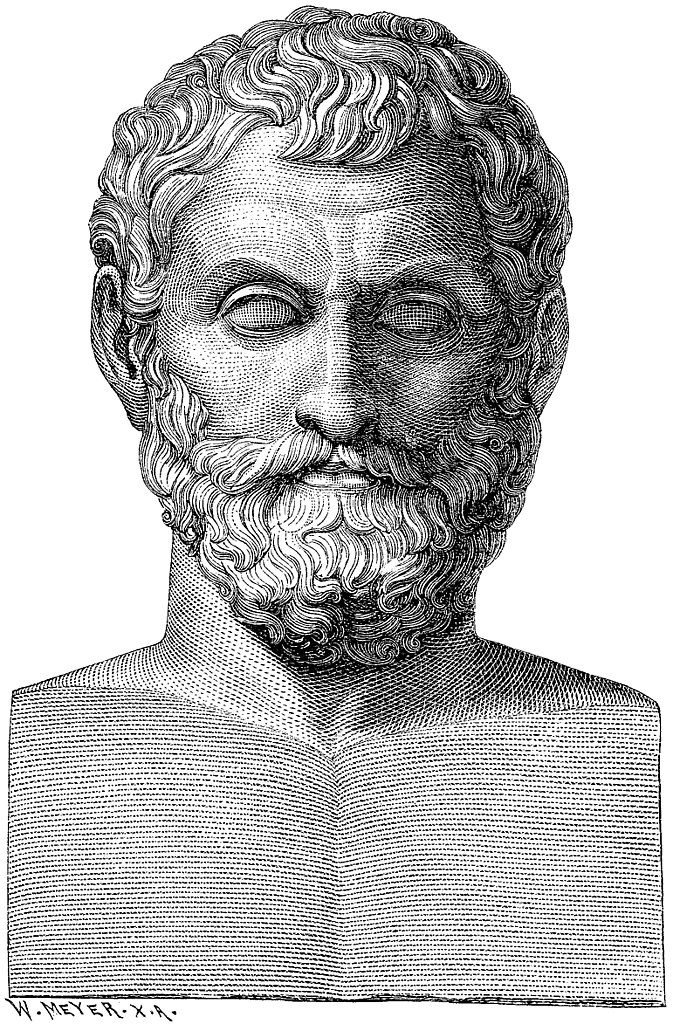

Sophistic Greek Philosophy
The Sophists were a group of travelling teachers who traveled throughout Greece in the 5th and 4th centuries BCE. They taught various subjects, including rhetoric, mathematics, and logic. The Sophists were known for their innovative and sometimes controversial ideas, and for their skills as public speakers. Some of the most famous Sophists include Protagoras, Gorgias, and Hippias.
Classical Greek Philosophy
Classical Greek philosophy refers to the philosophical developments of the most famous philosophers in all of ancient Greece, including Socrates, Plato and Aristotle.
Socrates, who lived in Athens in the 5th century BCE was one of the most famous ancient Greek philosophers. Socrates was a philosopher who was primarily concerned with ethics and morality. He believed that the path to wisdom was through questioning and that by asking questions, one could gain a better understanding of the world and one’s place in it.
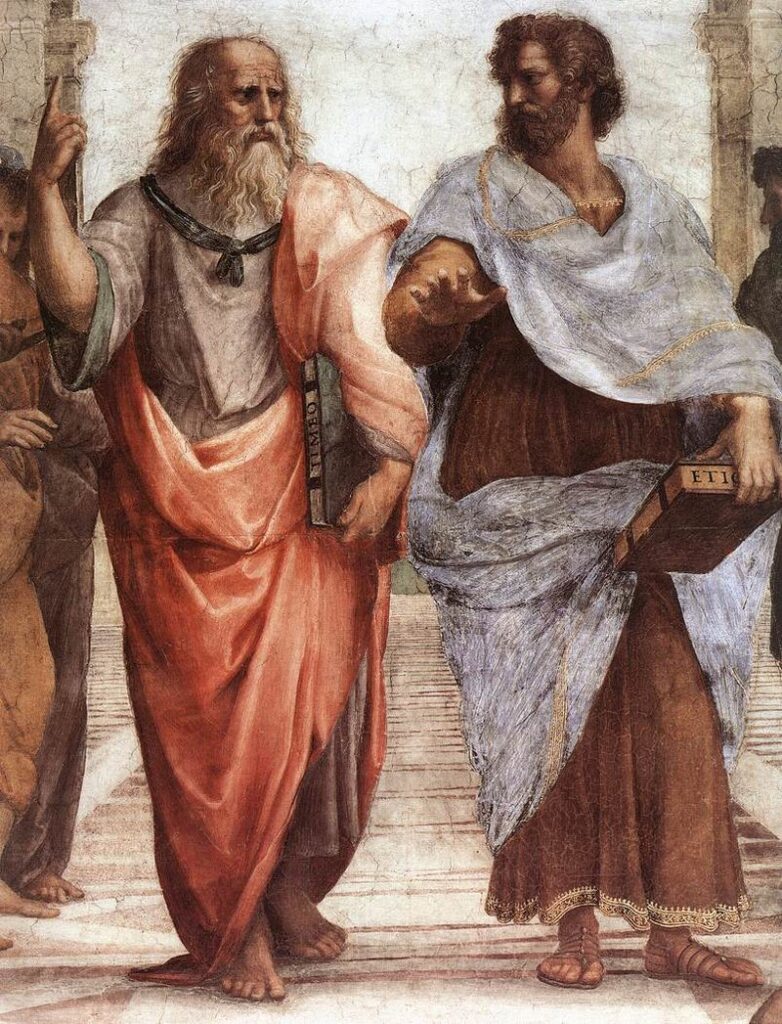
Plato was a student of Socrates and one of the greatest philosophers in the Western tradition. He founded the Academy in Athens, which was one of the first institutions of higher learning in the Western world. Plato was primarily concerned with metaphysics and epistemology, and he believed that knowledge was innate and that the purpose of life was to seek truth and wisdom.
Aristotle was a student of Plato and one of the greatest philosophers in the Western tradition. He was primarily concerned with ethics and politics, and he believed that the ultimate goal of life was happiness, which could be achieved through reason and virtue. Aristotle was also a scientist and made important contributions to the fields of biology, physics, and psychology.


Hellenistic Philosophy in Ancient Greece
The Hellenistic period in Ancient Greece was marked by the spread of Greek culture and ideas throughout the Mediterranean world. This period saw the rise of new schools of philosophy, such as the Stoics and the Epicureans, which were concerned with ethics and the nature of the universe.
Significance of Ancient Greek Philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy covered a wide range of topics, including ethics, politics, science, and metaphysics. The ideas of these ancient philosophers have had a profound influence on Western culture and thought and continue to be studied and discussed today.
In summary, philosophy in Ancient Greece developed over several centuries. It covered a wide range of ideas and thinkers, and is considered the foundation of Western philosophy. The ancient Greek philosophers were interested in understanding the world and human nature, and their ideas have had a profound influence on Western culture and thought.