Classical Greece refers to the period of about 200 years in ancient Greek history from the 5th to the 4th centuries BCE. It is widely regarded as the birthplace of Western civilization. It was a time of great cultural, artistic, and political flourishing that greatly influenced the development of Western thought and culture. From the towering achievements of philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle to the stunning architectural masterpieces of the Parthenon and the Acropolis, Classical Greece left an incredible mark on the world. In this article, we will explore the history, culture, and achievements of classical Greece and why it remains so important today.
Geography of Classical Greece
Classical Greece was centered around the major city-states of ancient Greece that were located in the southern part of the Balkan Peninsula. The two most powerful city-states were Athens and Sparta, and their rivalry dominated the political landscape of of the time. Despite their differences, the city-states shared a common language, religion, and cultural heritage, and they cooperated in times of crisis, such as the Greco-Persian Wars.
The geography of Classical Greece was characterized by rugged mountains and rocky coastline, which helped to shape the distinctive culture of the region. The abundant olive groves and fertile valleys provided ample agricultural resources, while the warm climate allowed for outdoor activities such as theater, sports, and philosophical discourse. The Aegean Sea, which surrounded the city-states of ancient Greece, was a vital source of commerce and played a critical role in the spread of ancient Greek culture and ideas throughout the ancient world.

Politics of Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a time of great political change and experimentation. The city-states were each ruled by a unique form of government, including: monarchies, oligarchies and democracies. Athens is famous for being the birthplace of democracy, a system of government in which power is held by the people. The Athenian democracy was a direct democracy, in which citizens could vote on laws and political decisions directly, rather than through representatives. Despite its many flaws and limitations, the Athenian democracy was a major step forward in the development of Western political thought and remains an important milestone in the history of democracy.
Sparta, on the other hand, was a military oligarchy, ruled by a small group of warriors known as the Spartans. The Spartans were renowned for their military prowess and discipline, and they dominated the political landscape of classical Greece through their military power. Despite their reputation as warriors, the Spartans also placed a strong emphasis on education and physical fitness, and their rigorous training regime produced some of the most capable soldiers in the ancient world.
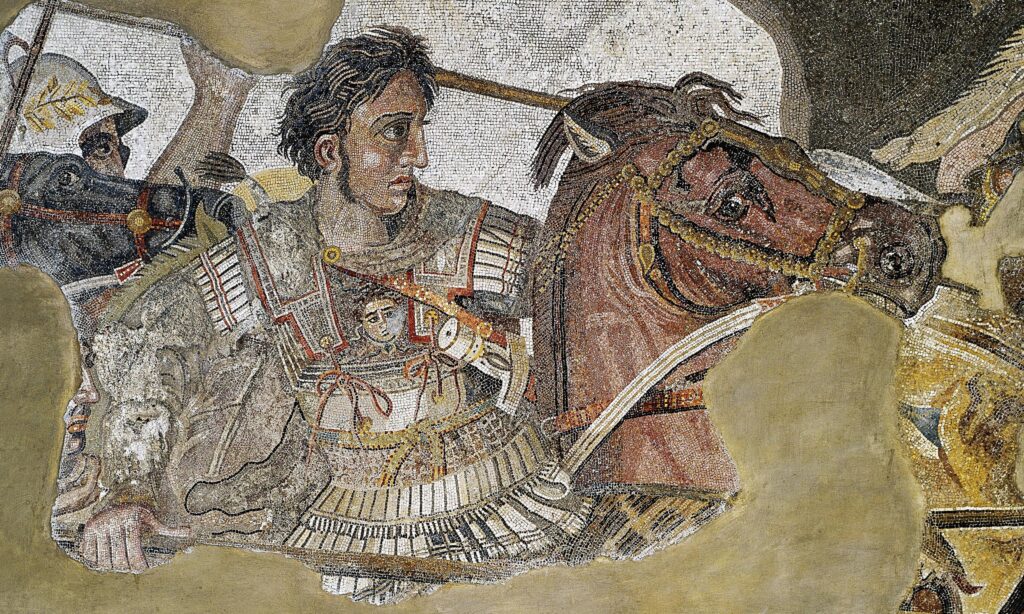
As well, the timeframe of Classical Greece includes the period in which Philip II of Macedon united the city-states of ancient Greece. Philip II was the father of Alexander the Great, who famously conquered large sections of ancient Greece, Persia and India. In fact, the Classical Greek period is considered to have ended when Alexander the Great died in 323 BCE. The period that came after Classical Greece is referred to as ‘Hellenistic Greece‘.

Culture of Classical Greece
Classical Greece is also known for its cultural achievements, which include significant contributions to art, literature, philosophy, and science. The Greek philosophers Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle are well known for their contributions to the development of Western philosophy, and the Greek playwrights Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides are well known for their contributions to the development of Western literature. Classical Greece is also known for its contributions to science and mathematics. The Greek mathematician Euclid is known for his contributions to geometry, and the Greek scientist Archimedes is known for his contributions to mathematics and physics.
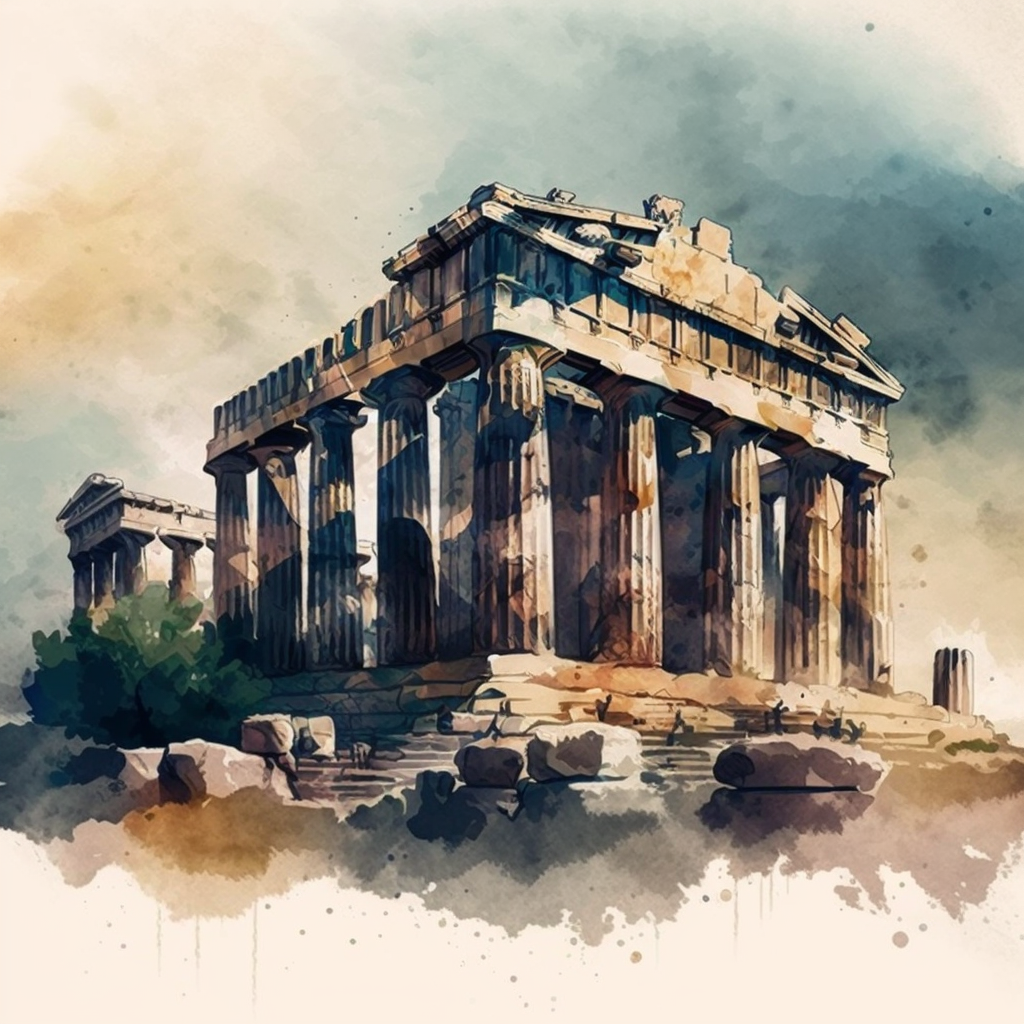
Furthermore, Classical Greece is remembered today for its contributions to ancient Greek architecture. The Parthenon, a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena, is considered one of the greatest architectural achievements of Classical Greece and stands as a testament to the talent and skill of the ancient Greek architects and sculptors.

Significance of Classical Greece
Overall, Classical Greece was a time of great cultural achievements and political change in ancient Greece. The city-states of Athens and Sparta emerged as the two most powerful states and made important contributions to art, literature, philosophy, and science. It was also a time of political change, as the city-states of ancient Greece were eventually united under the rule of Philip II of Macedon, and the included the rise to power of Alexander the Great.