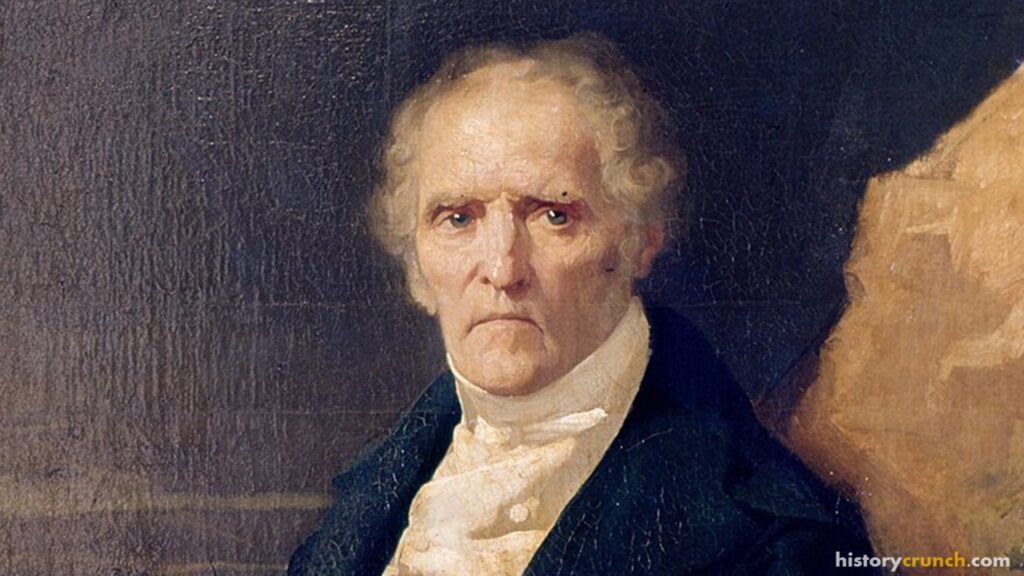
Charles Fourier, born on April 7, 1772, in Besançon, France, was a radical social thinker and one of the founders of utopian socialism. His innovative ideas on cooperative living, labor organization, and social reform challenged the societal norms of his time and inspired future generations of social reformers. His ideas had a profound impact on the Industrial Revolution and the development of socialism.
CHARLES FOURIER – EARLY LIFE
Fourier was born on April 7th, 1772, in Besançon, France. His father, a cloth merchant, ensured that Fourier received a good education, which included studies at the local Jesuit college. Despite his family’s wealth, Fourier was deeply critical of the mercantile system and the social injustices he observed.
CHARLES FOURIER – UTOPIAN SOCIALIST
Charles Fourier is credited with being an early Utopian Socialist similar to Robert Owen. He wrote several works related to his socialist ideas which centered on his main idea for society: small communities based on cooperation. In general, Fourier believed that poverty was one of society’s great issues and that it ultimately led to many other problems. He argued against the idea of competition in society, which is a principle of laissez-faire capitalism, and instead supported the idea that society should be more cooperative. Cooperation is the idea that citizens in a country should work towards a common goal rather than competing against each other.

To achieve this goal, Fourier proposed the creation of relatively small communities that were self-contained and ran on the principle of cooperation. He argued that a society that was based on cooperation would improve life for all people in society, and not just the wealthiest. Today, these types of communities are referred to as co-operatives, whereas Fourier referred to them as ‘phalanxes’. In his view, these communities were constructed with a central living quarters or apartments, in which all people in the community lived together. People’s work in the community was determined by their interests and was compensated based upon people’s willingness to do that work. For example, work that people generally disliked doing received high pay. Fourier’s ideas ended up spreading around the world and influenced people to develop their own communities based on cooperation. For example, in the United States, the community of Utopia, Ohio was established in 1844 by followers of Fourier. The followers built the community in hopes of building the ‘perfect community’ which is why they named it Utopia. In the community, the followers were charged $25 per year for a house on a small parcel of land; however the community remained collectively owned by all of the community members. Unfortunately, Utopia only last 3 years due to a flood in 1847, which devastated the community. Regardless, Fourier’s impact was significant as his ideas helped lead to the development of several cooperative-based communities across the world.

CHARLES FOURIER – DEATH AND LEGACY
He died at the age of 65 on October 10th, 1837 in Paris, France. Today, Fourier is remembered as an early socialist and is often referred to as a Utopian Socialist along with Robert Owen. He is credited with introducing socialist ideas into Europe that helped transform society during the Industrial Revolution.