The Enclosure Movement, a pivotal yet contentious period in agricultural history, fundamentally transformed rural landscapes, economies, and societies in England from the 16th century through the 19th century. This article explores into the origins, history, and outcomes of the Enclosure Movement, especially in relation to the events of the Industrial Revolution.
WHAT WAS THE ENCLOSURE MOVEMENT?
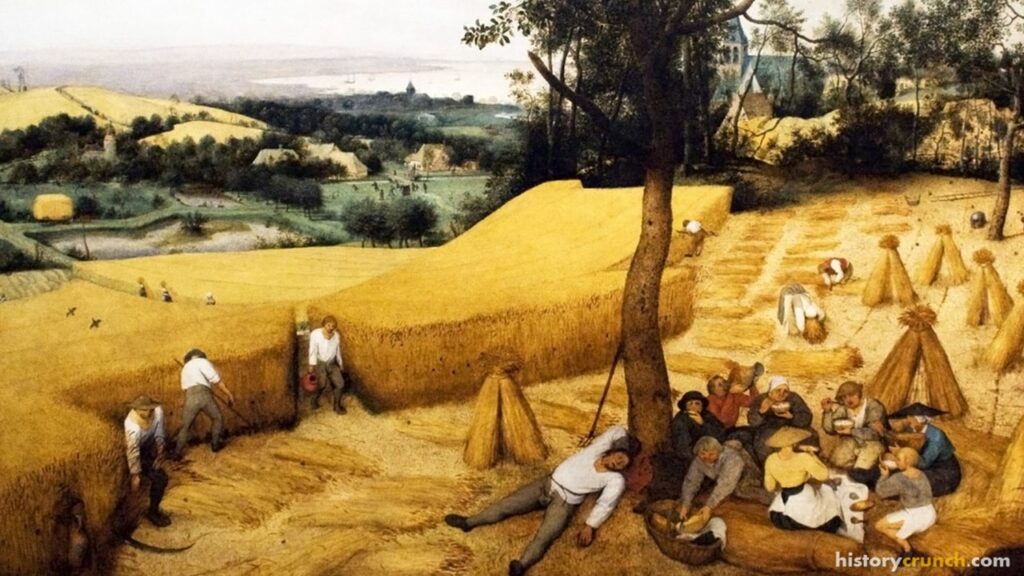
The Enclosure Movement refers to the process in England by which communal lands traditionally held in the open field system were combined into individual, privately-owned plots of land. This was often achieved through Acts of Parliament and also by informal agreements. Previously, lands in villages were collectively farmed in an open-field system, where villagers shared common lands for grazing livestock and growing crops. This process of ‘enclosure’ became especially common during the time of the British Agricultural Revolution and the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries.

ENCLOSURE MOVEMENT AND THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
The Industrial Revolution had several causes, but one of the most important was the impact of the British Agricultural Revolution. The British Agricultural Revolution many involved innovations in farming that led to a dramatic increase in food production. For example, Charles Townshend’s idea of crop rotation allowed farmers to grow more food, while Jethro Tull’s seed drill allowed faster and more efficient farming practices. While these were important features of the Agricultural Revolution, there was another that also had a big impact on the Industrial Revolution.

Another important feature of the Agricultural Revolution was the Enclosure Movement. In the decades and centuries before the 1700s, British farmers planted their crops on small strips of land while allowing their animals to graze on common fields shared collectively. However, in the 1700s, the British parliament passed legislation, referred to as the Enclosure Acts, which allowed the common areas to become privately owned. This led to wealthy farmers buying up large sections of land in order to create larger and more complex farms. Ultimately, this forced smaller farmers off of their land. Having lost their way of life, many of these farmers went to local towns and cities in search of work. This was important to the overall Industrial Revolution, because it helped create a system that created a large workforce for the factories and mines.
In general, the Enclosure Movement involved the British parliament passing a series of acts that allowed increased private ownership, which was a key characteristic of the Industrial Revolution. It forced the poor people to migrate to centralized locations such as industrial cities and towns and to seek work in factories and mines. Therefore, historians often view it as one of the main causes of the Industrial Revolution.

IMPACTS OF THE ENCLOSURE MOVEMENT
As stated above, the Enclosure Movement caused farmers to adopt more intensive and innovative farming methods. Crop rotation, selective breeding, and the use of machinery became possible on enclosed lands, leading to increased productivity and the ability to support more populous areas. This shift was important in supporting the growing urban populations of the Industrial Revolution.
With that said, one of the most significant economic impacts of the Enclosure Movement was the creation of a ‘landless working class’. As communal lands were enclosed, many rural farmers lost their means of subsistence, which forced them to seek employment in the newly created factories of the Industrial Revolution. This led to a mass migration of people to urban areas, which was important in providing the labor force required for industrial growth but also led to overcrowded cities and poor living conditions.