Abraham Lincoln won the presidential election of 1860 as the Republican candidate. He ran on a platform that opposed the expansion of slavery into new territories, which was a controversial issue at the time. His victory, without carrying a single Southern state, highlighted the deep divide that existed in the United States. In fact, historians consider Lincoln’s election to be significant in the eventual outbreak of the American Civil War.
WHO WAS ABRAHAM LINCOLN?
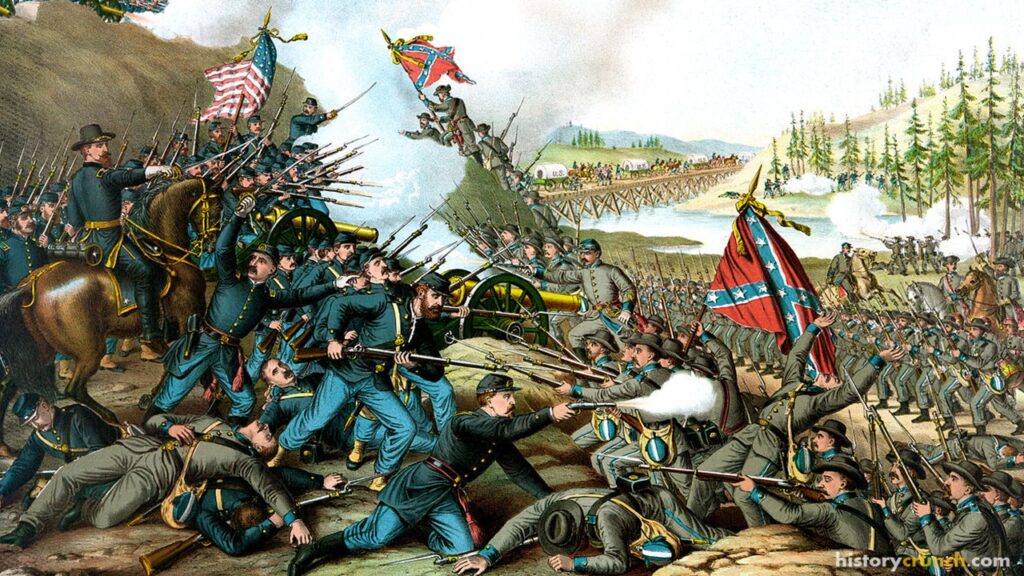
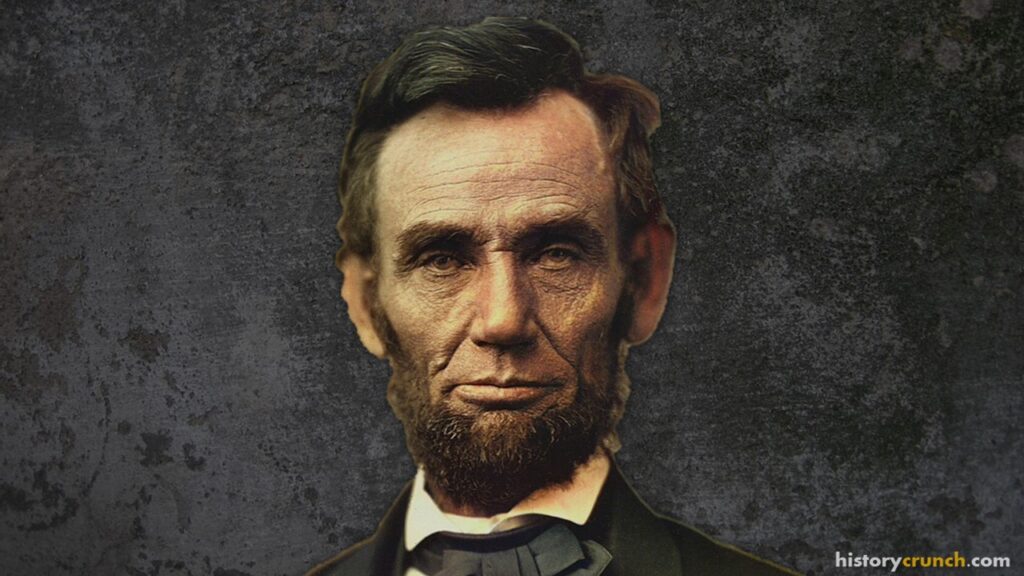
Abraham Lincoln is one of the most significant people in all of American history. He was the 16th President of the United States and served in office from March 4th, 1861 until April 15th, 1865 when he was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth. As President, Abraham Lincoln led the country through some of its most conflicted moments. For instance, he was President during the American Civil War, which saw the Northern states (Union) face off against the Southern states (Confederacy) in a series of bloody battles. As well, he dealt with the issue of slavery in the United States and eventually led the United States towards abolishing its practise. His election victory in 1860 was a very significant event, which historians consider to be one of the main causes for the outbreak of the Civil War in 1861.
Abraham Lincoln rose to be a prominent figure of the Republican Party throughout the late 1850s and early 1860s due to his eloquent speeches and views on slavery. For instance, on February 27th in 1860 Lincoln gave the famous ‘Cooper Union Speech’ in New York City. In the speech, Lincoln argued against slavery in the United States on moral grounds and that it was not the intention of the Founding Fathers of the United States to protect slavery. In the speech, Lincoln addressed how division between the Northern and Southern states was impacting the country and argued in favor of protecting the Union.

ABRAHAM LINCOLN’S PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION OF 1860 – SUMMARY
Abraham Lincoln gained the Republican nomination for President on May 18th of 1860 at the Republican National Convention, which was held in Chicago, Illinois. Hannibal Hamlin of Maine was chosen to be Lincoln’s Vice President candidate. During the campaign for the 1860 Presidential election, Lincoln faced off against three other candidates. The Democratic Party of the Northern states nominated Stephen Douglas, which Lincoln had faced off against in 1858 for the Illinois Senate seat. Lincoln ultimately lost that election but had gained the necessary experience to increase his political standing. The Democratic Party of the Southern states nominated John C. Breckinridge. At the time, the Democratic Party was facing a crisis in that the Southern states did not agree with Stephen Douglas’ stance on slavery. As such, in 1860 the Democratic Party nominated two candidates for president. Finally, a third party called the Constitutional Union Party, nominated John Bell.
Throughout the lead up to the 1860 election, Lincoln did little actual campaigning. Instead, the Republican Party organized the campaign efforts and particularly focused on young voters. As well, the campaign team for Lincoln gained support for Lincoln by producing many campaign posters and pamphlets. Ultimately, the hard work paid off and Lincoln was elected the 16th President of the United States on November 6th in 1860. He was the first Republican President in United States history and received over 1.8 million votes which represented 39.8% of the total. Although this was a strong victory for Lincoln, the 1860 election highlighted the divided nature of the United States at the time. For example, Lincoln received almost no support from the Southern states. In fact, there was not a single ballot cast for Lincoln in 10 out the 15 Southern states. As such, many historians point to Lincoln’s election as a significant factor in the eventual outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861.
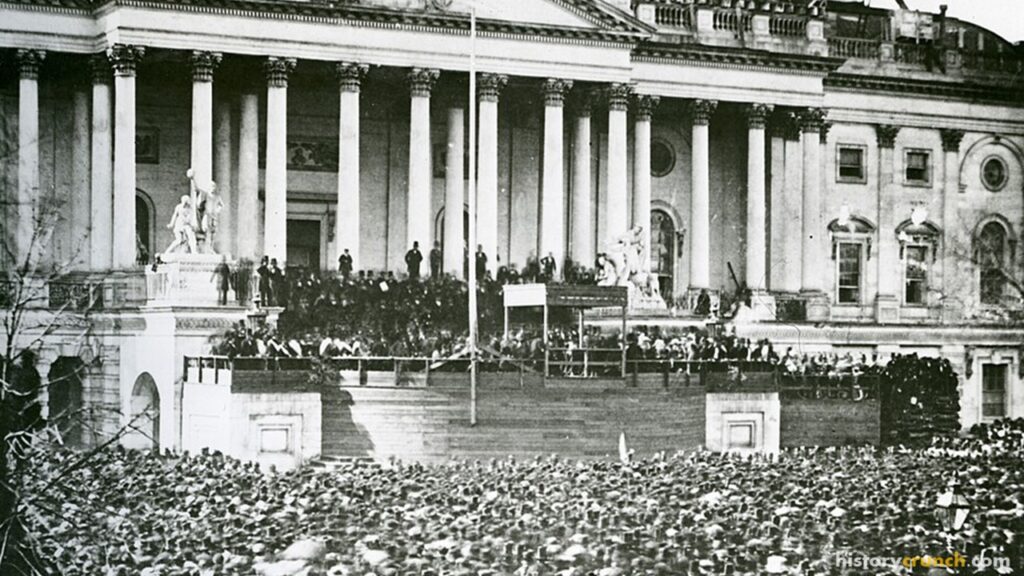

Abraham Lincoln is often referred to as one of the greatest presidents in the history of the United States. This is remarkable, considering that much of his time as President was marked by the events of the American Civil War and a divided nation. Following his November 6th, election victory, Abraham Lincoln was set to take office in March of 1861. Almost immediately, the Southern states began to express anger over Lincoln’s election and began to talk of secession. This means that the Southern states were seeking to leave the Union and break off from the Northern states. In fact, before Lincoln was inaugurated the following states seceded and formed the Confederate States of America: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina and Texas. Jefferson Davis was selected as the new President of the Confederacy. For his part, Lincoln tried to decrease the tensions at the time by trying to reach a compromise with the Southern states to protect slavery in states where it had long been established. He also addressed the crisis facing the country when he gave his inaugural address on March 4th, 1861:
“Apprehension seems to exist among the people of the Southern States that by the accession of a Republican Administration their property and their peace and personal security are to be endangered. There has never been any reasonable cause for such apprehension. Indeed, the most ample evidence to the contrary has all the while existed and been open to their inspection. It is found in nearly all the published speeches of him who now addresses you. I do but quote from one of those speeches when I declare that “I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so.”

Ultimately though, the tensions between the North and South could not be lessened and no compromise was reached. As a result, the United States was set on course for the outbreak of the American Civil War. Therefore, many historians argue that the election of Abraham Lincoln was a major cause of the Civil War, as it enflamed the already tense divide that existed in the nation.