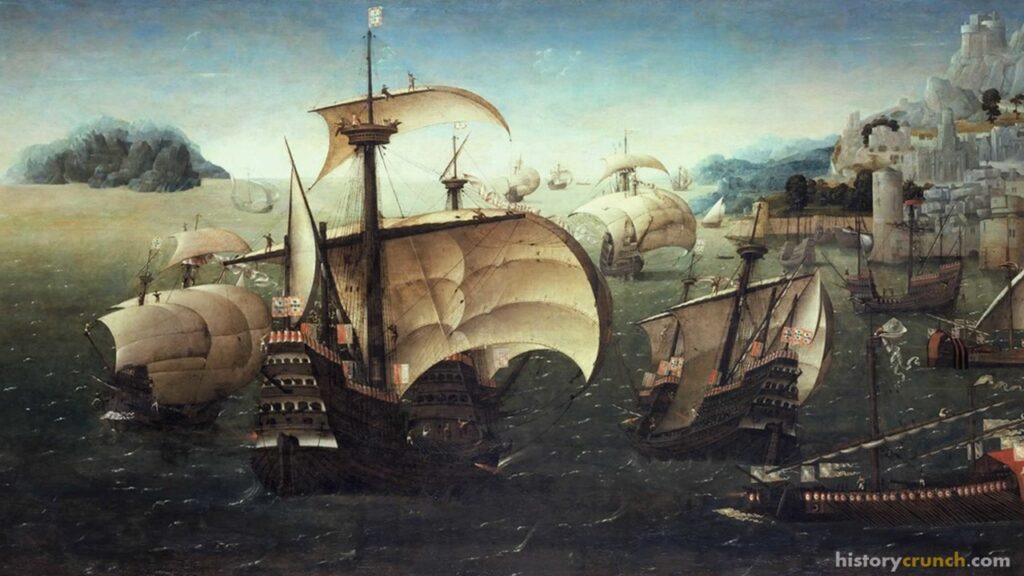
The Age of Exploration, or Age of Discovery, is one of the most important events in the history of the western world. It began in the early 15th century and continued until the end of the 17th century, and involved European explorers using their navigational skills to travel the world. In general, the Age of Exploration occurred for several different reasons, particularly in the countries of Portugal, Spain, France and England. During this time, these European nations launched expeditions that led to the ‘discovery’ of new lands, the expansion of trade routes, the rise of colonial empires, and the first phase of globalization.
AGE OF EXPLORATION – CAUSES
The Age of Exploration was caused by a combination of a few factors, including: trade, European monarchs, navigation, and curiosity. Together, these factors inspired European explorers to brave the dangerous journeys across the globe during the Age of Exploration.
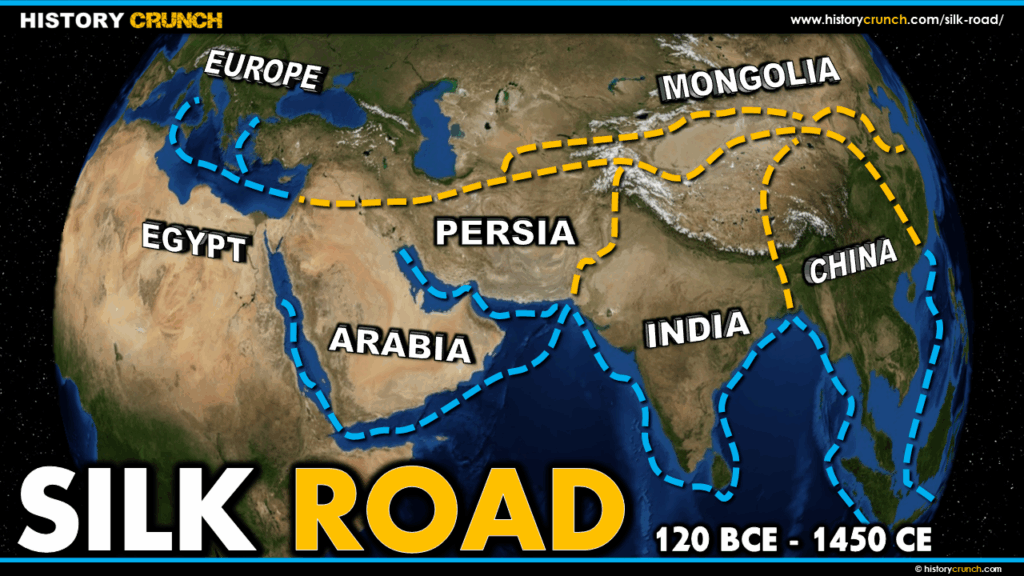
First, European countries were seeking new trade routes to distant trading partners in the Far East, including: China, India and Japan. European countries had traditionally traded with these countries through the Silk Road. The Silk Road was mostly over land and took merchants a great deal of time to ship goods. European countries were interested in speeding up trade by finding a quicker sea route.
A second reason for the beginning of the Age of Exploration was the rise of absolute monarchies in Europe. The powerful monarchs of Europe had centralized the authority and wealth of each country and used their vast wealth to fund the expeditions of many explorers. For example, Christopher Columbus was funded by King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain.
Third, Europeans had made some dramatic improvements in their navigational skill and technology that allowed early explorers to travel further and more accurately at sea. For example, ship building had drastically improved in the years immediately before the Age of Exploration began. New ships, such as the carrack and the caravel, allowed explorers to hold more cargo and the venture further than ever before.
The final reason for why the Age of Exploration began is because Europeans of the time were interested in foreign cultures and goods. In general, the Renaissance in Europe caused an expansion of new ideas and new understandings of the world. Europeans were interested in learning about these new ideas and expanding on their worldviews.
AGE OF EXPLORATION – MAJOR EVENTS
The Age of Exploration unfolded as a series of major events that were led initially by Portugal and Spain, followed by England and France. Each of these countries experienced the same forces that pushed them to explore the world, but they also shared one important characteristic. They were all countries that bordered on the Atlantic Ocean and had easy access to the sea with many sea ports and experienced sailors. This allowed these four nations to have the ability to begin exploring while other European nations did not.
PORTUGAL IN THE AGE OF EXPLORATION
Portugal is considered to have started the Age of Exploration ahead of the other main three nations with the expeditions that were carried out under Prince Henry the Navigator. Although he never directly carried out any trips of his own, Henry was vital in Portugal’s earliest trips and for revolutionizing the way that these trips were recorded. He set up a school of navigation in 1419 and under his direction sailors perfected sailing techniques, navigational tools, designs for sails and different mapping techniques. For example, he is credited with being the first to require captains of ships to keep a record or log of their journeys. This was important because it allowed different explorers to combine their findings to build up a common knowledge base of discoveries.
Early Portuguese explorers travelled south along the western coast of Africa in search of a new route to India and China in the early 1400s. These early explorers were so successful that Lisbon, the capital of Portugal, became the main trade center of Europe at the time. Famously, explorer Bartolomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1488. Next, Vasco da Gama reached India in 1498, establishing the first sea route from Europe to Asia. As a result, the Portuguese soon built trading posts and colonies along the African coast and India.

SPAIN IN THE AGE OF EXPLORATION
Portugal’s neighbor, Spain, was jealous of Portugal’s expeditions and the resulting wealth and wanted to begin its own explorations. Instead of heading south, like Portuguese sailors, Spanish explorers headed west across the Atlantic Ocean. These early explorers were seeking a quicker trade route to the Far East, including China and India.
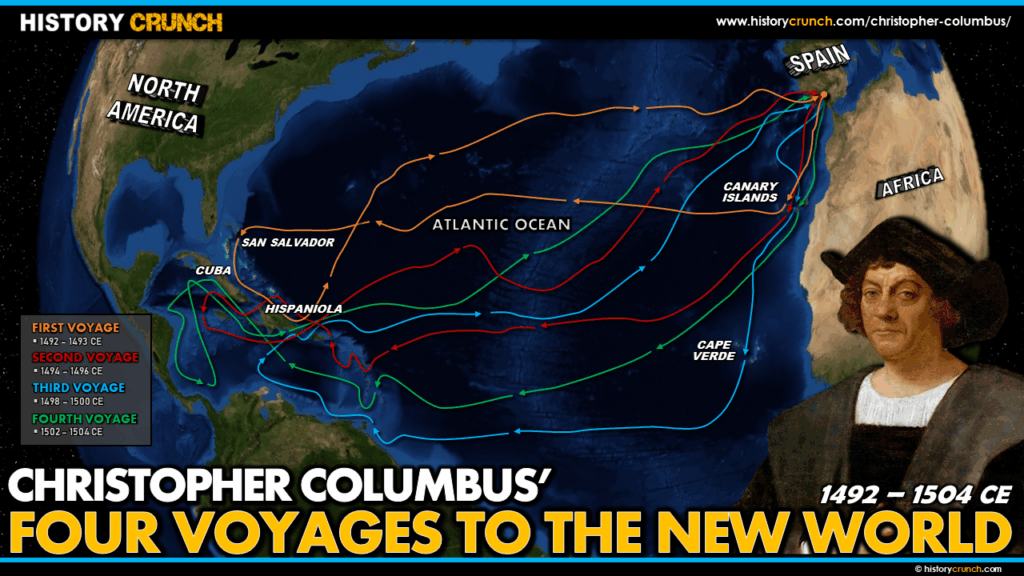
The most famous example of early Spanish explorers is Christopher Columbus. Columbus, while being of Italian nationality, sailed for Spain after being funded by the king and queen of Spain. He is credited with being the first European to explore the New World in 1492 (besides the Vikings 500 years earlier) and with beginning the wave of European settlement into the Americas. Another important venture by Spain, was in 1519, when Ferdinand Magellan began the first circumnavigation of the globe, which was ultimately completed by his crew in 1522. Spain conquered large parts of the Americas during the Age of Exploration. For instance, two famous conquests of the Americas, including: Hernán Cortés’ conquest of the Aztec Empire, and Francisco Pizarro’s conquest of the Inca Empire.
ENGLAND IN THE AGE OF EXPLORATION
Despite financing the voyage of John Cabot to Newfoundland in 1497, England did not show major interest in exploration until the late 1500s. By this time, both Spain and Portugal had become incredibly wealthy from their own expeditions and England wanted to gain land and wealth for itself. Many of the earliest English explorers voyaged to the New World and established colonies that England controlled as part of its vast empire. Most of these colonies were established along the eastern seaboard of modern-day Canada and the United States.

FRANCE IN THE AGE OF EXPLORATION
Similar to England, France was inspired to begin exploring in the 1500s during the Age of Exploration after seeing the wealth of both Spain and Portugal increase. Most of France’s expeditions focused on the areas of the St. Lawrence River in Canada. For example, Jacques Cartier famously explored the region for France and established an early colony for the French empire.
The Age of Exploration ended in the early 17th century after technological advancements and increased knowledge of the world allowed Europeans to travel easily across the globe by sea. In addition, the creation of settlements along the coasts of the newly found areas created a network of communication and trade, therefore ending the need to search for trade routes.

AGE OF EXPLORATION – SIGNIFICANCE
The Age of Exploration was a highly significant event in world history. First, the Age of Exploration led to a massive exchange between Europe and the New World. Historians refers to this as the Columbian Exchange, which was refers to the transfer of plants, animals, people, diseases, and ideas between the Old World and the New World. This exchange radically altered diets, economies, and populations worldwide. While it enriched Europe and transformed global agriculture, it also led to the devastation of indigenous populations, particularly in the Americas, due to disease and conquest.
Second, the Age of Exploration led to the era of European colonial empires and the Age of Imperialism. For instance, Spain and Portugal established vast empires in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Meanwhile, England and France followed with their own colonial holdings. One of the most tragic outcomes was the rise of the Atlantic Slave Trade, in which millions of Africans were enslaved and transported to the Americas under horrific conditions to labor on plantations. As such, the Age of Exploration had profoundly negative impacts for the indigenous peoples of the New World. For example, the Aztec, Inca, and many Native American societies were destroyed or radically transformed. In fact, it is now estimated that millions died due to disease, warfare, and forced labor.
The Age of Exploration also had a profound impact on scientific knowledge and technological advancements. For instance, it led to improvements in cartography, navigation, and ship design. Furthermore, cultural exchanges influenced art, literature, and science. As a result, historians consider the Age of Exploration to be significant to the events of the Renaissance.





